A mixer-first sliding-IF architecture has been chosen by a PhD student to create a 300GHz radio receiver front-end using 300GHz Ft (450GHz Fmax) transistors from a 130nm SiGe BiCMOS process. According to the thesis of Sumit Singh, studying at University of Oulu in Finland, down-conversion of the 300GHz carrier is initially by a local oscillator at two-thirds of the carrier, ...
Research
The latest electronics research news from within the industry and universities from around the world.
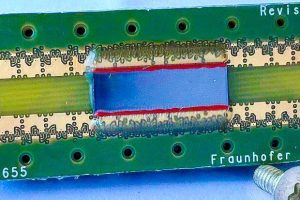
MEMS ultrasonic transducers key to detecting deep vein thrombosis
German research incubator Fraunhofer IPMS is working on a portable cuff that can be used to detect deep vein thrombosis (DVT) using ultrasound scanning from CMUTs – capacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducers. “They are considered to be the next generation of medical ultrasound sensors,” according to Fraunhofer. “The low-cost mass production of CMUTs makes them widely available. Their advantages, such as ...
TDK: ‘1,000Wh/L solid-state battery’
TDK claims to have developed a solid-state battery that can hold 1,000Wh/litre, as a replacement for coin cells. “Utilising proprietary material technology, TDK has managed to develop a material for the new solid-state battery with a significantly higher energy density than TDK’s conventional mass-produced CeraCharge solid-state batteries, due to the use of oxide-based solid electrolyte and lithium alloy anodes,” according ...
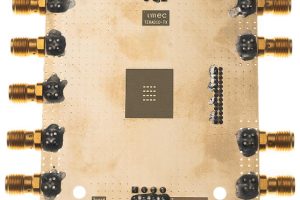
56Gbit/s zero-IF D-band beam-forming transmitter for 120-145GHz comms
Imec unveiled a CMOS 56Gbit/s zero-IF D-band beam-forming transmitter at the IEEE RFIC Symposium in Washington. “It is a key component of a 4-way beamforming transceiver chip currently being developed by imec’s researchers,” according to the Belgian research lab. “With this technology, they aim to support the deployment of short-range wireless services at frequencies above 100GHz.” It sees Gbit/s communication ...
2D template stabilises Perovkite for solar cells
Formamidinium lead iodide perovskite solar cells can be made to run for 1,000 hours at 85°C while loosing under 3% efficiency, according to Rice University. “Right now, we think that this is state-of-the-art in terms of stability,” said Rice engineer Aditya Mohite (right). The key was to grow its FAPbI3 from a solution containing a custom two-dimensional perovskite, designed to ...
Canada joins Square Kilometre Array Observatory as tenth Member
Canada has joined the Square Kilometre Array Observatory (SKAO) as a Member and becomes the tenth country to join the intergovernmental organisation. It also announced a $269m investment over eight years in the radio astronomy project. The National Research Council of Canada’s (NRC) Herzberg Astronomy and Astrophysics Research Centre will oversee the investment and will be working with Canadian industrial ...
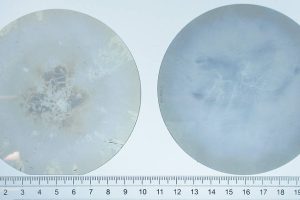
99% usable 100mm AlN wafers for UVC LEDs
Crystal IS has reached 99% usable area in the 100mm diameter single-crystal aluminum nitride substrates that it is developing for UVC LED production, particularly in the 260 – 270nm germicidal range. The ultra-wide bandgap and high thermal conductivity of AlN is also applicable to RF and power devices. Its first 100mm AlN wafer was made in August last year, and ...
NI’s vision for hybrid AI
NI has set out its stall for AI in the test industry. Following the announcement of LabView AI assistant at the end of last year (currently in beta testing), CTO of technology and innovation, Kevin Shultz spoke to Electronics Weekly about what will be the role of AI in test. He explained that the increasing complexity of products being tested ...
What is the difference between MBE and MOCVD technologies?
Professor Richard Hogg and Dr Neil Gerrard compare molecular beam epitaxy and metal organic chemical vapour deposition film technologies. Molecular beam epitaxy (MBE) and metal organic chemical vapour deposition (MOCVD) are different types of epitaxial growth technologies used in III-V semiconductor synthesis. They both deposit atoms onto a substrate or semiconductor wafer, one atomic layer at a time. They produce ...
Leicester University, ispace work on lunar night survival technology
The University of Leicester is working with ispace, the Japanese space transportation specialist, to develop lunar night survival technology. They will collaborate on different approaches that could benefit future ispace lunar lander and rover missions. For example, they will be investigating, the use of radioisotope heater units to provide enough heat for a spacecraft through a lunar night, which has ...
 Electronics Weekly Electronics Design & Components Tech News
Electronics Weekly Electronics Design & Components Tech News